To create a new relationship between two tables, click Relationship on the toolbar and then click parent and child tables in your diagram.
In this example, click table customer and then table order.
The new relationship line appears in the diagram and column customer_id is added to the child table order automatically.
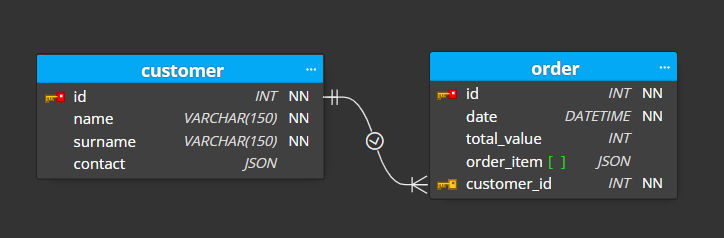
By default, the primary key is used for the relationship. If you wish to change the primary key, select the parent table and modify the primary key.
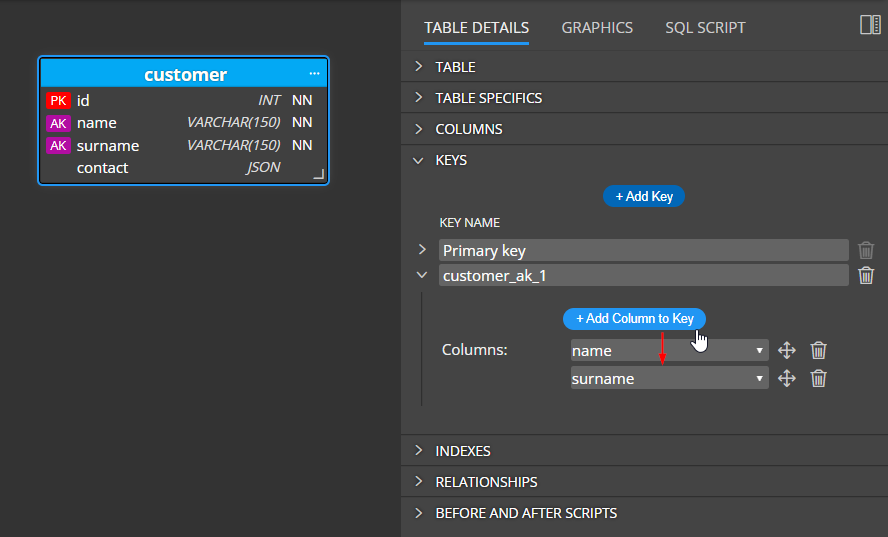
To create a new alternate key, click the +Add key button in section Keys.
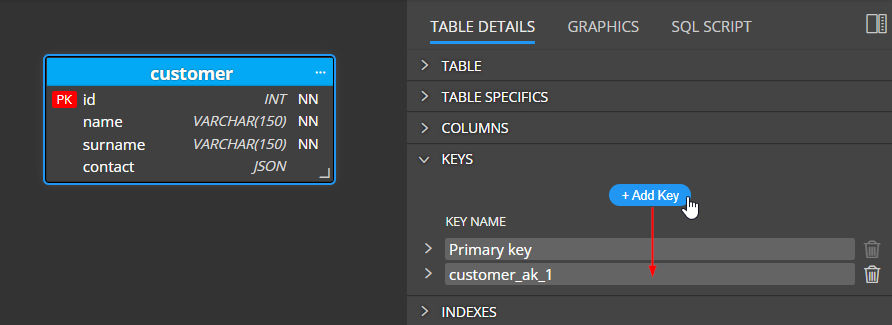
The new key appears in the child table. Click +Add Column to Key and select a column.
Compound keys
In case you need to create a compound key, for example, a key that should contain columns name and surname, repeat the process twice.
Usage
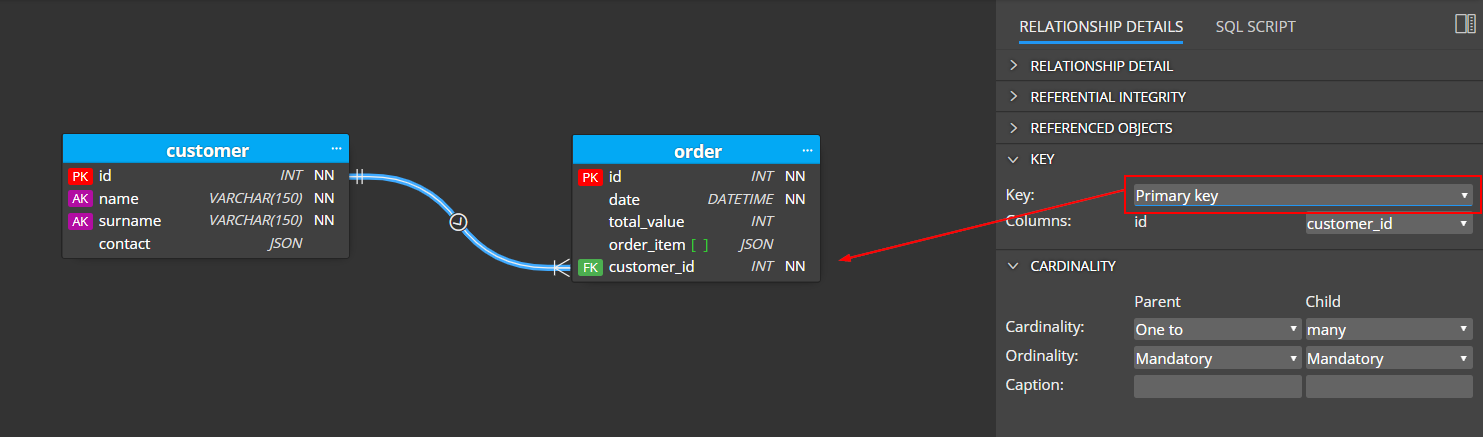
To use the compound/alternate key instead of the primary key, select the relationship and navigate to section Key.
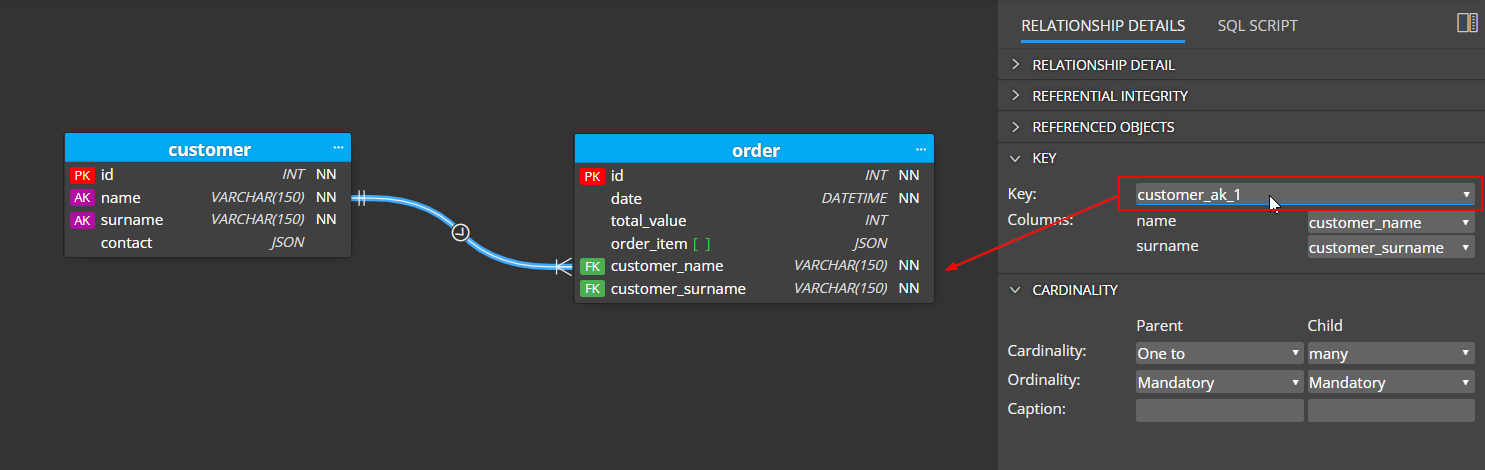
Change the value in the key dropdown to the new alternate key name. The tool removes the customer_id column from the child table and adds there both the columns defined in the alternate key: customer_name and customer_surname.
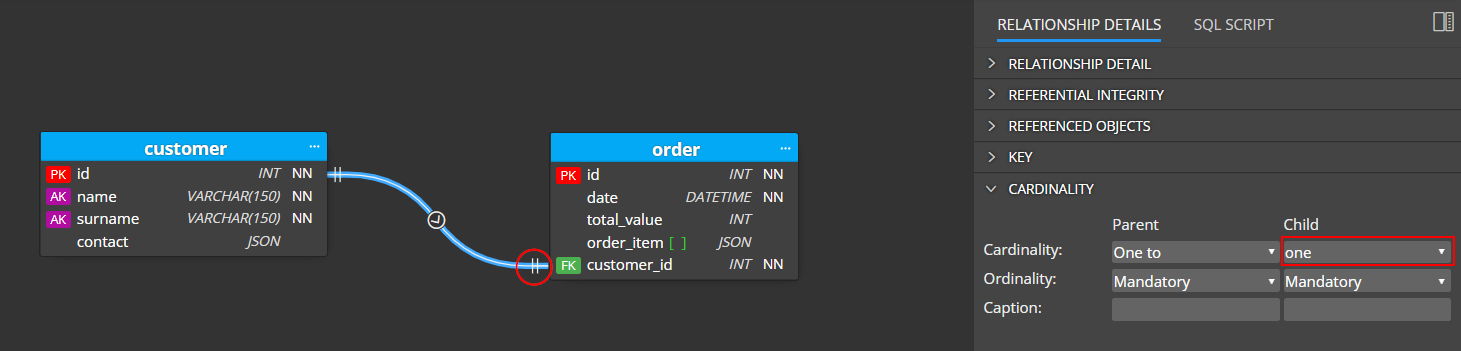
Cardinality
Cardinality settings affect the display of relationships in your diagram. Select a relationship and change values in section Cardinality.
Optional child settings change the appearance of line ending to circle. And if you set cardinality to one, the relationship line will be displayed without the crows’ foot notation graphics.
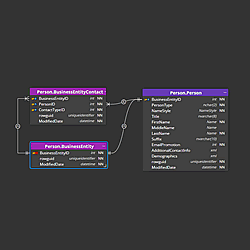
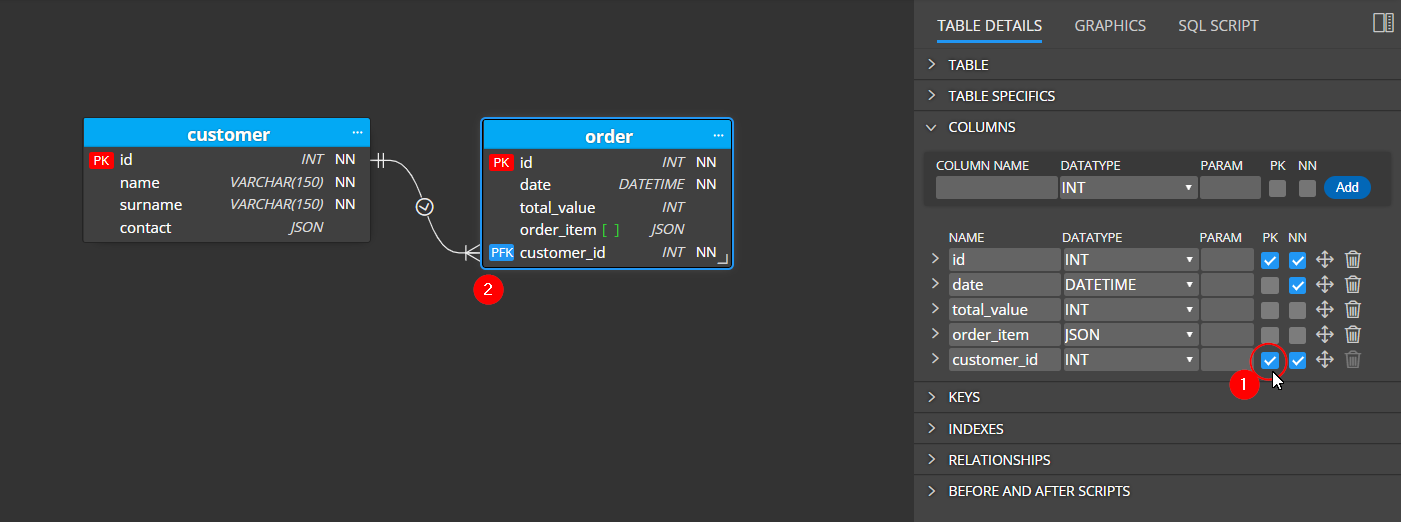
Primary foreign keys
If you set a foreign key column in a child table to the primary key, the color of the key/graphics changes to blue.
Referential integrity
To change referential integrity settings, select a relationship and modify values in section Referential integrity.
Self relationships
To create a self-relationship, click the Relationship item on the toolbar and then click one table in the diagram twice (not double click it, wait a moment before you click the same table again.)
#